 Backing Up Databases
Backing Up Databases 
Regularly back up your data and redo log entries from the data and log areas of your database to data carriers. No downtime is required for backups: you can execute backups in the ONLINE operational state, meaning that the database is available to users during backups.
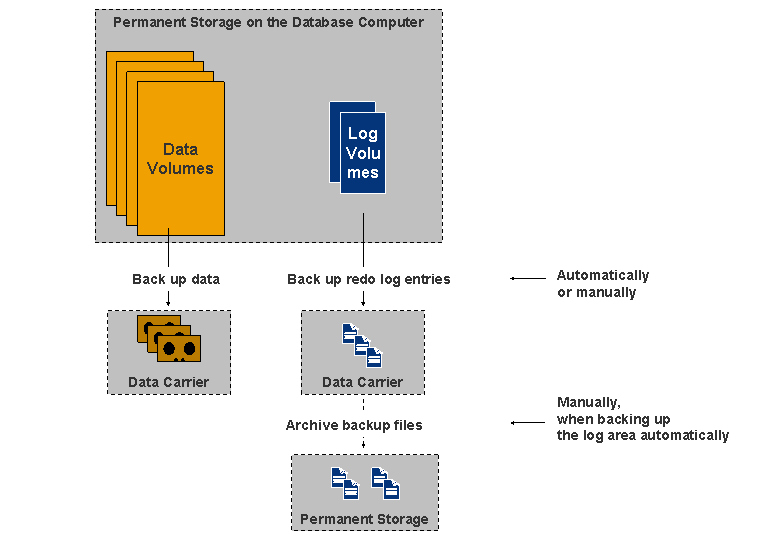
Backing Up: Schematic Overview
If there is a database failure due to a hardware defect or a logical error, you can restore the database to a consistent state by importing the data and log entries from the backups. You can use backups you created on a Microsoft Windows system on Unix and Linux systems, and vice versa.
Procedure
For backing up, use Database Studio, Database Manager CLI or CCMS (in SAP systems only). Not that neither data exports created with the Loader database tool nor data area snapshots are data backups: they are not suitable for restoring a database.
 Recommendation
Recommendation
Test the backup and restore process on a test computer before starting up your productive system.
Make a plan of when you want to perform backups.
More information: Periodic Administration Tasks
Define backup templates.
More information: Backup Templates and Data Carriers
Regularly back up data and redo log entries during normal database operation.
More information:
To speed up the backup process, you can back up the data on several data carriers in parallel.
More information: Backing Up to a Group of Parallel Data Carriers
You can also back up data to data carriers on remote computers.
More information: Backing Up and Restoring Data with Remote Computers
You can use backup tools from third-party providers.
More information: Using Third-Party Backup Tools
Check if the database system carried out the backup successfully.
More information: Monitoring Databases
If you use data carriers of the FILE type for log backups (backup files), then archive the backup files regularly.
More information: Archiving Backup Files
More Information
Concepts of the Database Systems, How Databases Store Data and Log Entries