 Starting or Stopping Databases
Starting or Stopping Databases 
In normal operation, databases are in the ONLINE operational state. You can either manually start databases (transfer them to the ONLINE operational state), or activate automatic startup.
To perform certain administration tasks such as restoring a database after a system failure, the ADMIN operational state or a restart of the database may be required.
Prerequisites
You are logged on to the database as database system administrator or as a DBM operator with server authorization for starting and stopping the database.
More information: Glossary, Server Permission
Make sure that no users are logged on to the database.
Procedure
Transferring Databases to a Different Operational State
Select the database in the explorer tree.
In the context menu of the database, choose .
Choose the operational state.
Database Operational States Icon
Operational State
Description

ONLINE
The database is running. Database users can log on and execute SQL statements. The database system administrator and DBM operators can perform administrative tasks.
-
STANDBY
For standby databases in hot standby systems only
Note that you cannot connect to a standby database. It is in a constant restart state.
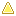
ADMIN
The database is only available for administration tasks.
OFFLINE
The database is not running.
Starting Databases
Transfer the database to the ONLINE operational state.
Restarting Databases
Transfer the database to the OFFLINE and then to the ONLINE operational state.
Starting Special Kernel Variants
 Note
Note
This function is for development and testing purposes only. Do not use it for regular database operations.
In the context menu of the database, choose
Choose the kernel variant.
Kernel Variants Kernel Variant
Description
fast
System default
Fastest kernel variant, with minimum logging and runtime checks
slow
Kernel variant with extensive logging and runtime checks
Do not use this kernel variant during production operation of the database.
test
Kernel variant which was developed especially for test purposes
Do not use this kernel variant during production operation of the database.
More Information
Database Administration, Activating Automatic Database Start
 Administration Tasks
Administration Tasks  Set State
Set State