 Managing Users
Managing Users 
Before you can work with the database, you must log on using a database tool or via an interface. When you log on, you identify yourself with a user name and authenticate your identity with the corresponding password (authentication). After authentication, you can, within the scope of the authorizations assigned to you, access and work with data in the database.
The database system differentiates between the following types of users:
DBM operators who can manage databases
Database users who can change data in the database
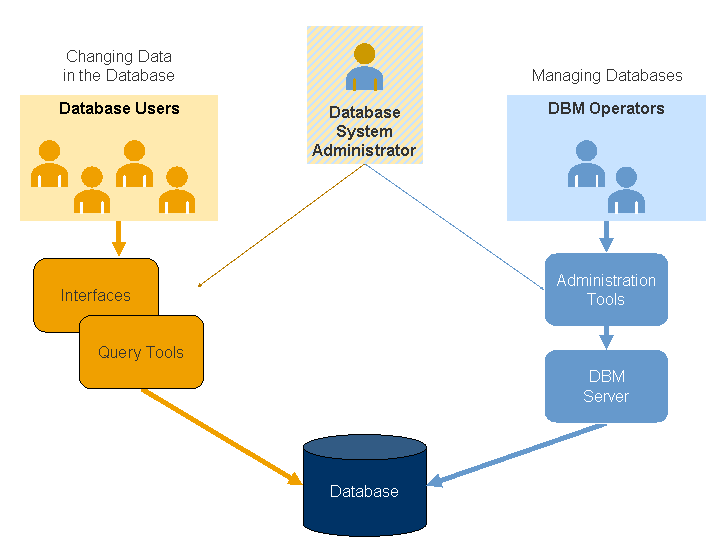
Overview of the Users of the Database System
When creating a database you create the database system administrator, the first DBM operator and, depending on the system, further standard users. You can add further users later.
Some naming restrictions apply. More information: Conventions for User Names and Passwords
Default Name |
Default Password(s) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
DBADMIN DBA (up to and including version 7.5) |
SECRET DBA (up to and including version 7.5) |
Database system administrator |
DBM |
SECRET DBM |
First DBM operator with all DBM server authorizations |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
SUPERDBA |
Database system administrator |
CONTROL |
DBM operator with all server authorizations |
SAPR3 |
In older SAP systems: Database administrator (database user of class DBA) |
SAP<SAPSID> |
In newer SAP systems, in particular in MCOD systems (Multiple Components One Database): Database administrator for the SAP system with the ID <SAPSID> (database user of class DBA) |
SAP<SAPSID>DB |
In Java EE systems: Database administrator for the SAP system with the ID <SAPSID> (database user of class DBA) |
To protect database resources from direct access using operating system commands, special operating system users and groups are available. More information: Special Operating System Users and Groups
To simplify the logon process to databases with command line tools, you can save the logon data using the XUSER program. More information: XUSER documentation